Read JSON with codeable in Swift

Reading JSON data from local files and url is now much easier with codeable in Swift 5. This article shows how to load JSON data from a local file as well as from the open weather data api.
Open Weather
Open Weather provide a range of weather-related products accessed through API calls. There is a free tier available that will allow us to retrieve the current weather through the api for Current weather data.
Create local JSON file
An empty file is added to the project with the name of the weatherData.json. We are going to focus on the Current Weather data. The sample JSON data from the current whether API call is copied to the JSON file.
1{
2 "coord": {
3 "lon": -122.08,
4 "lat": 37.39
5 },
6 "weather": [
7 {
8 "id": 800,
9 "main": "Clear",
10 "description": "clear sky",
11 "icon": "01d"
12 }
13 ],
14 "base": "stations",
15 "main": {
16 "temp": 282.55,
17 "feels_like": 281.86,
18 "temp_min": 280.37,
19 "temp_max": 284.26,
20 "pressure": 1023,
21 "humidity": 100,
22 "sea_level": 100
23 },
24 "visibility": 16093,
25 "wind": {
26 "speed": 1.5,
27 "deg": 350
28 },
29 "clouds": {
30 "all": 1
31 },
32 "dt": 1560350645,
33 "sys": {
34 "type": 1,
35 "id": 5122,
36 "message": 0.0139,
37 "country": "US",
38 "sunrise": 1560343627,
39 "sunset": 1560396563
40 },
41 "timezone": -25200,
42 "id": 420006353,
43 "name": "Mountain View",
44 "cod": 200
45}
Define Swift object for the JSON data
It is helpful to define Swift Structs to contain the main data from the JSON objects. It is not necessary to define elements for all of the items in the JSON file.
1struct WeatherRawData : Codable {
2 var name: String
3 var timezone: Double
4 var weather: [WeatherData]
5 var main: MainData
6 var wind: WindData
7 var clouds: CloudsData
8
9 struct WeatherData: Codable {
10 var id: Double
11 var main: String
12 var description: String
13 var icon: String
14 }
15
16 struct MainData: Codable {
17 var temp: Double
18 var feels_like: Double
19 var temp_min: Double
20 var temp_max: Double
21 var pressure: Double
22 var humidity: Double
23 }
24
25 struct WindData: Codable {
26 var speed: Double
27 var deg: Double
28 }
29
30 struct CloudsData: Codable {
31 var all: Double
32 }
33}
Load the JSON data from the file
The JSON data is loaded from the file when the application is launched. A file loader
class with a static function to load the JSON data is added to the app. Loading the
JSON file is split into two functions; the first locates the file and loads the
contents into a Data object; the second uses JSONDecoder to decode the JSON
data into a WeatherRawData object.
1class FileLoader {
2
3 static func readLocalFile(_ filename: String) -> Data? {
4 guard let file = Bundle.main.path(forResource: filename, ofType: "json")
5 else {
6 fatalError("Unable to locate file \"\(filename)\" in main bundle.")
7 }
8
9 do {
10 return try String(contentsOfFile: file).data(using: .utf8)
11 } catch {
12 fatalError("Unable to load \"\(filename)\" from main bundle:\n\(error)")
13 }
14 }
15
16
17 static func loadJson(_ data: Data) -> WeatherRawData {
18 do {
19 return try JSONDecoder().decode(WeatherRawData.self, from: data)
20 } catch {
21 fatalError("Unable to decode \"\(data)\" as \(WeatherRawData.self):\n\(error)")
22 }
23 }
24}
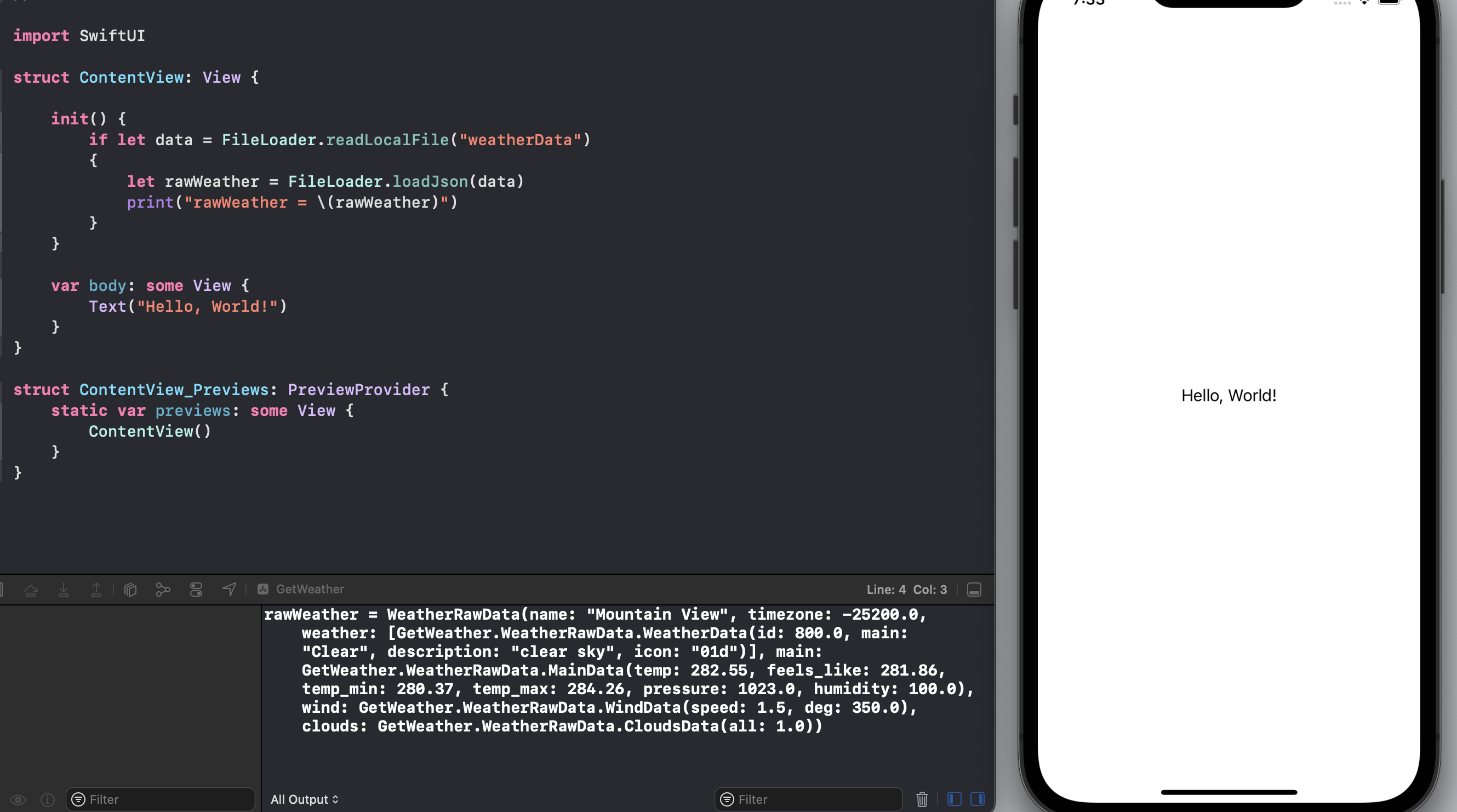
The print statement is used to ensure the file is loading and the JSON is being
decoded correctly into WeatherRawData.
1struct ContentView: View {
2 init() {
3 if let data = FileLoader.readLocalFile("weatherData")
4 {
5 let rawWeather = FileLoader.loadJson(data)
6 print("rawWeather = \(rawWeather)")
7 }
8 }
9
10 var body: some View {
11 Text("Hello, World!")
12 }
13}
Create Weather Model and ViewModel
It might be tempting to use the raw weather data directly in a Swift view, but this would lead to tightly coupled code that would be brittle. It is better to define a separate model for the Weather containing the data that is relevant to the App.
Weather Model
1struct WeatherModel {
2 var locationName: String
3 var weatherName: String
4 var description: String
5 var temperature: Double
6 var timeOffUtc: Double //timezone Shift in seconds from UTC
7
8 init (data: WeatherRawData) {
9 locationName = data.name
10 weatherName = data.weather.first!.main
11 description = data.weather.first!.description
12 temperature = data.main.temp
13 timeOffUtc = data.timezone
14 }
15}
Weather ViewModel
A weather ViewModel is added to separate the View from the Model. It is defined as a
class because it has to conform to ObservableObject protocol, which allows the
view in SwiftUI to bind to the ViewModel. The weatherModel property is marked as
@Published so that whenever there are any changes to the model, all views using
that object will be reloaded to reflect those changes. There is more detail on
MVVM in MVVM in SwiftUI.
1class WeatherViewModel: ObservableObject {
2 @Published private var weatherModel: WeatherModel
3
4 init() {
5 guard let data = FileLoader.readLocalFile("weatherData")
6 else {
7 fatalError("Unable to locate file \"weatherData.json\" in main bundle.")
8 }
9
10 let rawWeather = FileLoader.loadJson(data)
11 weatherModel = WeatherModel(data: rawWeather)
12 }
13
14 var location: String {
15 get { weatherModel.locationName }
16 }
17
18 var weatherMain: String {
19 get { weatherModel.weatherName }
20 }
21
22 var description: String {
23 get { weatherModel.description }
24 }
25
26 var temperature: Double {
27 get { weatherModel.temperature }
28 }
29
30 var locationTime: String {
31 get {
32 let utcDateFormatter = DateFormatter()
33 utcDateFormatter.timeZone = TimeZone(abbreviation: "UTC")
34 utcDateFormatter.timeStyle = .medium
35 let now = Date().addingTimeInterval(weatherModel.timeOffUtc)
36 let dateString = utcDateFormatter.string(from: now)
37 return dateString
38 }
39 }
40}
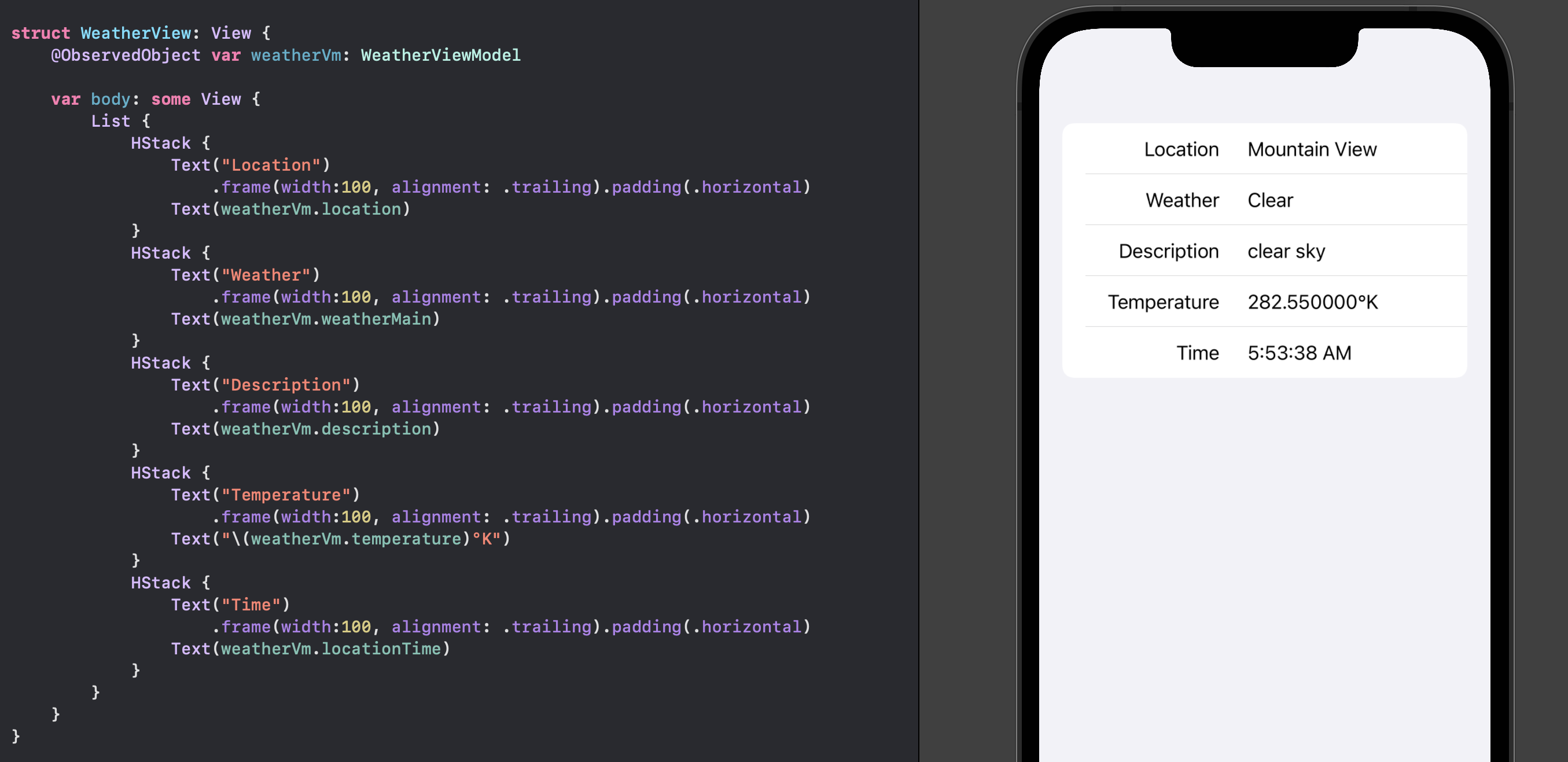
Weather View
The View has a property for the ViewModel and a new ViewModel is instantiated when
the App is launched. The weatherVm property is marked with the @ObservedObject
property wrapper, so the view can be notified when the state of the object has
changed. The view simply displays some of the weather data loaded from the JSON file.
1struct WeatherView: View {
2 @ObservedObject var weatherVm: WeatherViewModel
3
4 var body: some View {
5 List {
6 HStack {
7 Text("Location")
8 .frame(width:100, alignment: .trailing).padding(.horizontal)
9 Text(weatherVm.location)
10 }
11 HStack {
12 Text("Weather")
13 .frame(width:100, alignment: .trailing).padding(.horizontal)
14 Text(weatherVm.weatherMain)
15 }
16 HStack {
17 Text("Description")
18 .frame(width:100, alignment: .trailing).padding(.horizontal)
19 Text(weatherVm.description)
20 }
21 HStack {
22 Text("Temperature")
23 .frame(width:100, alignment: .trailing).padding(.horizontal)
24 Text("\(weatherVm.temperature)°K")
25 }
26 HStack {
27 Text("Time")
28 .frame(width:100, alignment: .trailing).padding(.horizontal)
29 Text(weatherVm.locationTime)
30 }
31 }
32 }
33}
Get Weather from Open Weather API
Define a WeatherService class with a static function to call the Current weather
data API and retrieve the weather data based on GPS coordinates. An API key is
needed from Open Weather, which is located in the account section. The data
returned from the API call is the same format as the sample data, so the loadJson
function is reused to decode the JSON data into WeatherRawData.
1class WeatherService {
2 static func getCurrentWeather(latitude: CLLocationDegrees,
3 longitude: CLLocationDegrees) async throws -> WeatherRawData {
4 // Set the API with the appId for OpenWeather
5 guard let url = URL(string: "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?lat=\(latitude)&lon=\(longitude)&units=metric&appid=\("xxx WEATHER API KEY xxx")") else {
6 fatalError("Missing url")
7 }
8
9 // Call the API asynchronously and wait for the response
10 let urlRequest = URLRequest(url: url)
11 let (data, response) = try await URLSession.shared.data(for: urlRequest)
12
13 guard (response as? HTTPURLResponse)?.statusCode == 200 else {
14 fatalError("Error retrieving weather data")
15 }
16
17 return FileLoader.loadJson(data)
18 }
19}
Weather ViewModel
Update ViewModel to hold the current city and call the
WeatherService.getCurrentWeather when the city is selected in the View. Add an enum
for a number of cities and a function to return GPS coordinates for each city. This
could possibly be changed to a dictionary or some other structure.
1class WeatherViewModel: ObservableObject {
2 @Published private var weatherModel: WeatherModel
3 private var _city: String
4
5 init() {
6 guard let data = FileLoader.readLocalFile("weatherData")
7 else {
8 fatalError("Unable to locate file \"weatherData.json\" in main bundle.")
9 }
10
11 let rawWeather = FileLoader.loadJson(data)
12 weatherModel = WeatherModel(data: rawWeather)
13 _city = "not set"
14 }
15
16 var location: String {
17 get { weatherModel.locationName }
18 }
19
20 var weatherMain: String {
21 get { weatherModel.weatherName }
22 }
23
24 var description: String {
25 get { weatherModel.description }
26 }
27
28 var temperature: Double {
29 get { weatherModel.temperature }
30 }
31
32 var locationTime: String {
33 get {
34 let utcDateFormatter = DateFormatter()
35 utcDateFormatter.timeZone = TimeZone(abbreviation: "UTC")
36 utcDateFormatter.timeStyle = .medium
37 let now = Date().addingTimeInterval(weatherModel.timeOffUtc)
38 let dateString = utcDateFormatter.string(from: now)
39 return dateString
40 }
41 }
42
43 var city: String {
44 get { return _city}
45 }
46
47 @MainActor
48 func weatherForCity(_ c:City) async {
49 _city = c.rawValue
50 let (lat, lon) = coordinates(for: c)
51
52 do {
53 let rawWeather = try await WeatherService.getCurrentWeather(latitude: lat, longitude: lon)
54 weatherModel = WeatherModel(data: rawWeather)
55 }
56 catch {
57 print("Error fetching weather with '\(c.rawValue)' City:\n \(error)")
58 }
59 }
60
61 private func coordinates(for city: City) -> (Double, Double) {
62 switch city {
63 case .newyork:
64 return (40.749939623101724, -73.98584035140507)
65 case .london:
66 return (51.48403374752388, -0.0059268752163408114)
67 case .paris:
68 return (48.8619958275662, 2.294848578874564)
69 case .vancouver:
70 return (49.2791749376975, -123.10359944424778)
71 case .capetown:
72 return (-33.96475307519853, 18.417554193804826)
73 case .sydney:
74 return (-33.85657055055687, 151.21537180010895)
75 }
76 }
77}
78
79enum City: String, CaseIterable, Identifiable {
80 var id: Self { self }
81 case newyork = "New York"
82 case london = "London"
83 case paris = "Paris"
84 case vancouver = "Vancouver"
85 case capetown = "Cape Town"
86 case sydney = "Sydney"
87}
Weather View
Add another view to display a number of buttons for different cities and the existing
WeatherView. The action on the city buttons needs to call the weatherForCity
function in the ViewModel asynchronously when the city is selected.
1struct WeatherView2: View {
2 @ObservedObject var weatherVm: WeatherViewModel
3
4 var body: some View {
5 VStack {
6 VStack {
7 Text("Current weather in Cities")
8 Button("New York") {
9 Task {
10 await weatherVm.weatherForCity(_: .newyork)
11 }
12 }
13 .buttonStyle(BlueButtonStyle())
14 Button("Cape Town") {
15 Task {
16 await weatherVm.weatherForCity(_: .capetown)
17 }
18 }
19 .buttonStyle(BlueButtonStyle())
20 }
21 .frame(width: 300)
22
23 WeatherView(weatherVm: weatherVm)
24 }
25 }
26}
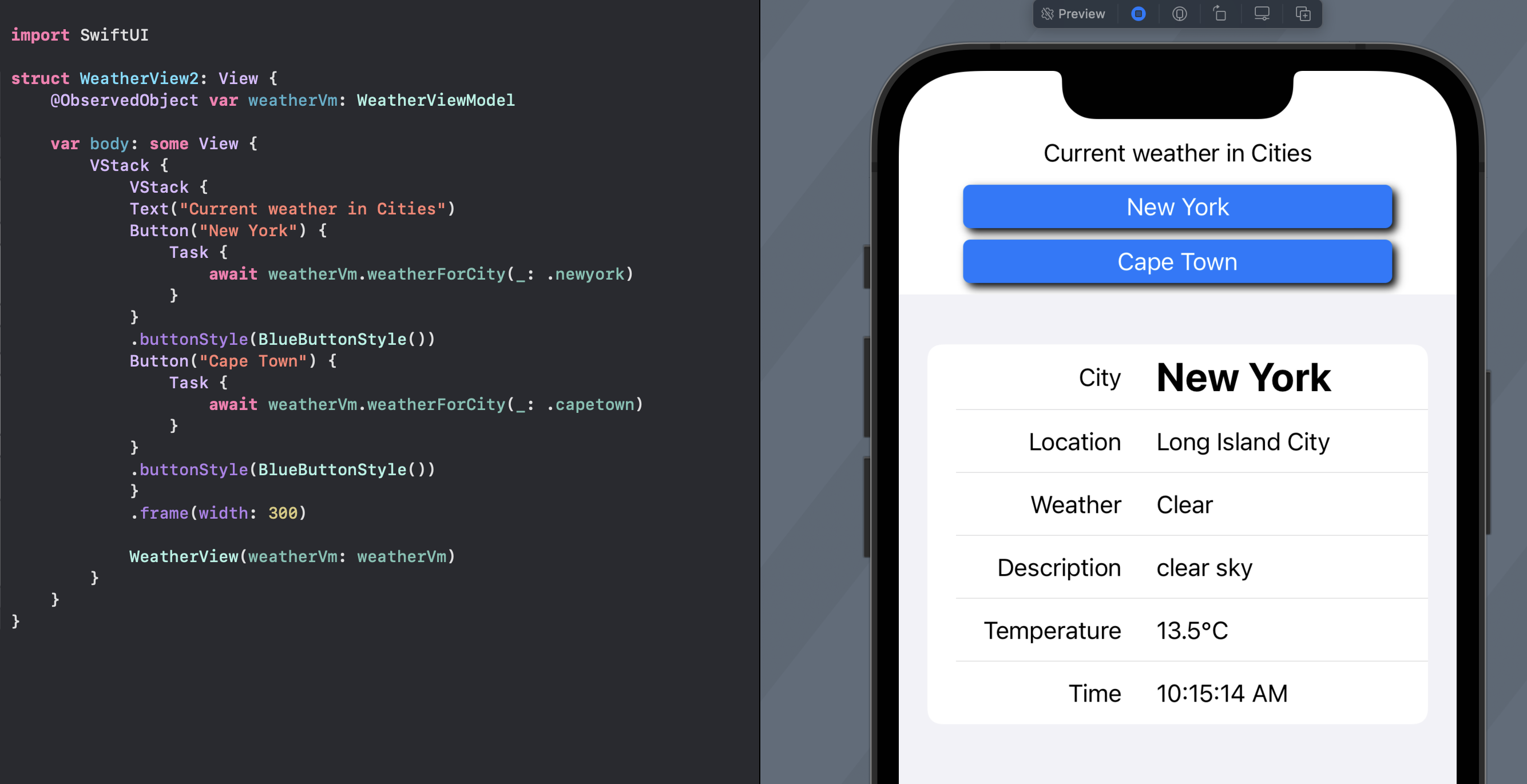
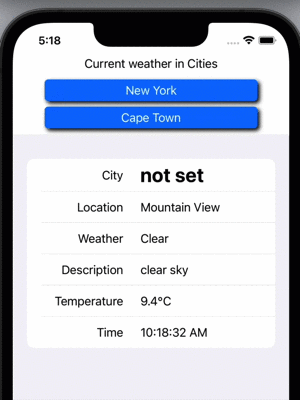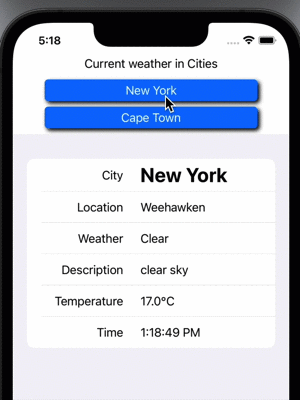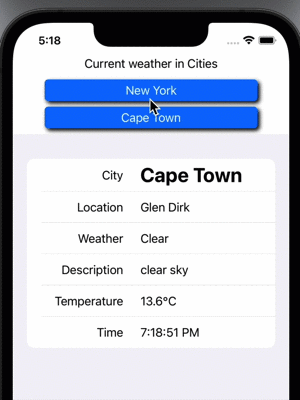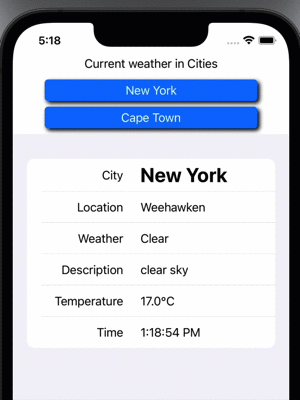
Display Weather from two cities
Conclusion
Parsing JSON content and loading into a Swift objects is straight forward using JSONDecoder. In this article, weather data was loaded, first from a local file in the app bundle, and then from a call to Open Weather API. Parsing the JSON data is the same whether the data originates from a local file or from a web API. Some of the weather data is simply presented in a list, this could be improved by displaying appropriate icons or images based on the weather conditions.